This group's name consists of two words: ‘Kham' is ‘gold' and ‘ti' means ‘place,' therefore the Khamti homeland is seen as a place of gold. They have long been viewed as one of Myanmar's ethnic groups, while in India they have gained status as one of that country's Scheduled (official) Tribes.
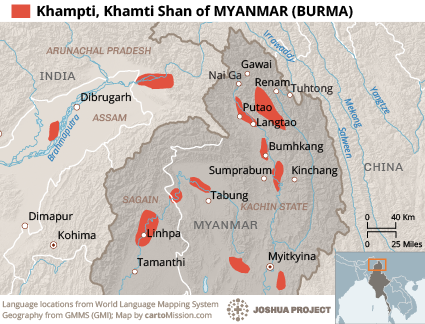
Location: The Khamti people, who number 9,000 in Myanmar and a further 21,000 in India, live in fertile areas with abundant natural resources. In northern Myanmar, most Khamti live in thickly forested areas within the Putao (4,500) and Myitkyina (3,500) districts in Kachin State, near the Chinese border. A smaller number are found in Hkamti District in neighboring Sagaing Region. Khamti communities in India, where their name is spelled “Khampti,” are located in the three northeast states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, and Manipur.
The Khamti language is part of the Southwestern Tai branch of the Kra-Dai linguistic family, related to other Tai languages such as Shan, Tai Nua, and further afield, to Lao in Laos and Thai in Thailand. Although the use of their language is widespread, most Khamti people in Myanmar now also speak Burmese or Kachin Jingpo as second languages, while in India more Khamti people now speak the Tibeto-Burman Adi language than their mother tongue. In Myanmar, the Khamti have their own orthography, called Lik-Tai, which originated from the Northern Shan script. It is preserved in thousands of ancient Buddhist manuscripts that have been carefully copied by the Khamti. Their written language has given the Khamti a sense of pride, solidifying their faith in Buddhism while causing them to shun new religions.
The Khamti first settled along the Chindwin River in the 1100s, and for centuries they ruled one of nine Tai-Shan principalities in northern Myanmar. Their principality was composed of “three small Khamti states and developed a highly advanced civilization. Those who escaped enslavement by the Burmese settled in their present locations in the fertile triangle of northern Myanmar.” The Khamti first migrated to India in 1751 to escape feudal oppression and clan warfare in their homeland. Until recently, “blood feuds were a common means of settling disputes. The family of the perpetrator were absolved only if they were prepared to recompense the murdered person's family properly for their loss: cowry shells for his teeth and nails, swords for his fingers and toes, rifles for his arms, slaves for his legs, and gongs for his head and mouth.”
Most Khamti people are engaged in agriculture, forestry, and fishing. Although almost all Khamti see themselves as devoted Buddhists, “they eat a variety of fish and consume the meat of fowls, pigs, goats, bears, deer, and tigers. Beef is a taboo.”4 The Khamti are skilled carvers, with many of their temples adorned with “figures of snakes, dragons, and other monsters, in wood, bone and ivory. They work in gold, silver, and iron, and they manufactured embossed shields of buffalo or rhinoceros hide.”
The blood feuds among the Khamti are said to have “stemmed from the people's belief in demons and spirits, which was just as strong as their devotion to Buddhism. In such animistic cults, blood sacrifice played an extremely important role…. The Khamtis still venerate the spirits of the family, the clan, and the village.” Despite living near strong Christian groups, including the Rawang, Lisu, and Kachin Jingpo, the Khamti have stubbornly held on to their Buddhist traditions and have spurned most attempts to evangelize them.
Mission work among the Khamti in India commenced in 1836 but enjoyed very little success due to their geographical isolation and strong faith in Buddhism. In Myanmar, American Baptist missionary George Geis and his wife settled in Myitkyina, but their work soon gravitated away from the Buddhist Khamti to the more receptive Kachin people. The Khamti New Testament was published in 2023, marking the first Christian Scripture ever produced for this fascinating group. It is hoped many Khamti will read it and desire to know the living God.
Scripture Prayers for the Khamti in Myanmar (Burma).
| Profile Source: Asia Harvest |